forked from ckan/ckan-docker
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request #130 from mjanez/ckan-2.9.11
Update Docker Compose files with new volume configurations
- Loading branch information
Showing
9 changed files
with
201 additions
and
130 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ To verify a successful Docker installation, run `docker run hello-world` and `do | |
| versions for client and server. | ||
|
|
||
| > [!NOTE] | ||
| > Learn more about [Docker](#docker-basic-commands)/[Docker Compose](#docker-compose-basic-commands) basic commands. | ||
| > Learn more about [Docker/Docker Compose](#docker-basic-commands) basic commands. | ||
| > | ||
|
|
||
|
|
@@ -209,31 +209,38 @@ See [CKAN images](#5-ckan-images) for more details of what happens when using de | |
| #### Create an extension | ||
| You can use the ckan [extension](https://docs.ckan.org/en/latest/extensions/tutorial.html#creating-a-new-extension) instructions to create a CKAN extension, only executing the command inside the CKAN container and setting the mounted `src/` folder as output: | ||
|
|
||
| docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml exec ckan-dev /bin/sh -c "ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini generate extension --output-dir /srv/app/src_extensions" | ||
|  | ||
| ```bash | ||
| docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml exec ckan-dev /bin/sh -c "ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini generate extension --output-dir /srv/app/src_extensions" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Then, answer the prompts to configure the plugin: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
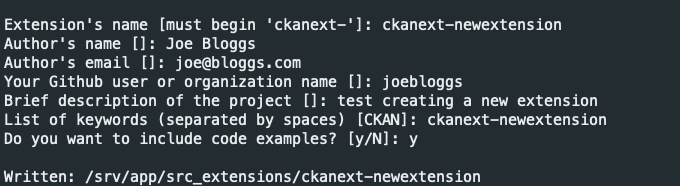
| Extension's name [must begin 'ckanext-']: ckanext-newextension | ||
| Author's name []: Joe Bloggs | ||
| Author's email []: [email protected] | ||
| Your Github user or organization name []: joebloggs | ||
| Brief description of the project []: test creating a new extension | ||
| List of keywords (separated by spaces) [CKAN]: ckanext-newextension | ||
| Do you want to include code examples? [y/N]: y | ||
| Written: /srv/app/src_extensions/ckanext-newextension | ||
| ``` | ||
| The new extension files and directories are created in the `/srv/app/src_extensions/` folder in the running container. They will also exist in the local src/ directory as local `/src` directory is mounted as `/srv/app/src_extensions/` on the ckan container. You might need to change the owner of its folder to have the appropiate permissions. | ||
| #### Running HTTPS on development mode | ||
| #### Running HTTPS on development mode | ||
|
|
||
| Sometimes is useful to run your local development instance under HTTPS, for instance if you are using authentication extensions like [ckanext-saml2auth](https://github.com/keitaroinc/ckanext-saml2auth). To enable it, set the following in your `.env` file: | ||
| ``` | ||
| ``` | ||
| USE_HTTPS_FOR_DEV=true | ||
| ``` | ||
| ``` | ||
| ```ini | ||
| USE_HTTPS_FOR_DEV=true | ||
| ``` | ||
| and update the site URL setting: | ||
| ``` | ||
| ``` | ||
| CKAN_SITE_URL=https://localhost:5000 | ||
| ``` | ||
| ``` | ||
| ```ini | ||
| CKAN_SITE_URL=https://localhost:5000 | ||
| ``` | ||
| After recreating the `ckan-dev` container, you should be able to access CKAN at https://localhost:5000 | ||
|
|
@@ -327,7 +334,6 @@ ckan | |
| ├── setup | ||
| ├── Dockerfile | ||
| └── Dockerfile.dev | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| > [!NOTE] | ||
|
|
@@ -337,6 +343,36 @@ ckan | |
| > * Shows any changes between the staging area and the repository: | ||
| > `git diff --staged [file]` | ||
|
|
||
| #### Applying patches in dev mode | ||
| To apply patches in development mode, you would need to follow these steps: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Ensure that your patches are placed in the [`ckan/patches`](/ckan/patches/) directory. The patches should be organized into subdirectories named after the package they are intended to patch (e.g., `ckan` or `ckanext-??`). Each patch file should end with the .patch extension. | ||
|
|
||
| For example, your directory structure might look like this: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| ckan | ||
| ├── patches | ||
| │ ├── ckan | ||
| │ │ ├── 01_datasets_per_page.patch | ||
| │ │ ├── 02_groups_per_page.patch | ||
| │ │ ├── 03_or_filters.patch | ||
| │ └── ckanext-harvest | ||
| │ └── 01_resubmit_objects.patch | ||
| ├── setup | ||
| ├── Dockerfile | ||
| └── Dockerfile.dev | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 2. Navigate to the [`/src`](/src/) directory. | ||
|
|
||
| 3. Apply the patches using the patch command: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| find /path/to/ckan/patches -name '*.patch' -exec patch -p1 < {} \; | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| This command will recursively search the `/path/to/ckan/patches` directory for files ending with `.patch` and apply them using the patch command. Replace `/path/to/ckan/patches` with the actual path to your `ckan/patches` directory. | ||
|
|
||
| ## ckan-docker addons | ||
| ### Debugging | ||
|
|
@@ -547,8 +583,8 @@ PostgreSQL offers the command line tools [`pg_dump`](https://www.postgresql.org/ | |
| 0 0 * * * /path/to/your/script/ckan_backup_custom.sh | ||
| ``` | ||
| > [!NOTE] | ||
| > Replace `/path/to/your/script` with the actual path to the `ckan_backup_custom.sh` script. | ||
| > [!NOTE] | ||
| > Replace `/path/to/your/script` with the actual path to the `ckan_backup_custom.sh` script. | ||
| 8. Save and close the file. | ||
|
|
@@ -605,89 +641,8 @@ If need to use a backup, restore it: | |
| ```bash | ||
| ckan -c ckan.ini user remove user_example` | ||
| ``` | ||
| ### Docker. Basic commands | ||
| #### Linux post-install steps | ||
| [These optional post-installation procedures](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/) shows you how to configure your Linux host machine to work better with Docker. For example, managing docker with [a non-root user](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/#manage-docker-as-a-non-root-user). | ||
| #### Configure Docker to start on boot | ||
| ```bash | ||
| sudo systemctl enable docker | ||
| # To disable this behavior, use disable instead. | ||
| sudo systemctl disable docker | ||
| ``` | ||
| #### Clear all Docker unused objects (images, containers, networks, local volumes) | ||
| ```bash | ||
| docker system prune # Clear all | ||
| docker system prune -a # Clear all (includes unused and dangling containers) | ||
| # By default, volumes are not removed to prevent important data from being deleted if there is currently no container using the volume. Use the `--volumes` flag when running the command to prune volumes: `docker system prune -a --volumes` | ||
| docker image prune # Clear unused images | ||
| docker container prune # Clear unused containers | ||
| docker volume prune # Clear unused volumes | ||
| docker network prune # Clear unused networks | ||
| ``` | ||
| ### Docker Compose. Basic commands | ||
| More info about Docker Compose commands at [docker compose reference](https://docs.docker.com/compose/reference/). | ||
| ```bash | ||
| # Basic. All containers or specific container: <container> | ||
| ## Starts existing containers for a service. | ||
| docker compose start <container> | ||
| ## Restarts existing containers/container for a service. | ||
| docker compose restart <container> | ||
| ## Stops running containers without removing them. | ||
| docker compose stop <container> | ||
| ## Pauses running containers of a service. | ||
| docker compose pause <container> | ||
| ## Unpauses paused containers of a service. | ||
| docker compose unpause <container> | ||
| # Display the logs of a container. Is it possible to retrieve only the last n seconds or other | ||
| docker logs [--since 60s] <container> -f | ||
| ## Lists containers. | ||
| docker compose ps | ||
| ## Remove all docker compose project | ||
| docker compose rm <container> | ||
| # Build. | ||
| ## Builds, (re)creates, starts, and attaches to containers for a service. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up | ||
| ## Build & up all the containers. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up -d --build | ||
| ## Build & up an specific container. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up -d --build <container> | ||
| ## To avoid using a cache of the previous build while creating a new image. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] build --no-cache | ||
| ## Build a project with a specific Docker Compose prefix. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] -p <my_project> up -d --build | ||
| ## Log the build | ||
| docker compose build --no-cache &> docker_build.log | ||
| # Down | ||
| # Stops containers and removes containers, networks, volumes, and images created by up. | ||
| docker compose [-p <my_project>] down | ||
| ``` | ||
| For more information about Docker and Docker Compose's basic commands and post-installation procedures, see [Docker/Docker Compose Info](./doc/info_docker.md) | ||
| ### Docker Compose. Configure a docker compose service to start on boot | ||
| To have Docker Compose run automatically when you reboot a machine, you can follow the steps below: | ||
|
|
||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,80 @@ | ||
| # Docker. Basic commands | ||
| ## Linux post-install steps | ||
| [These optional post-installation procedures](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/) shows you how to configure your Linux host machine to work better with Docker. For example, managing docker with [a non-root user](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/#manage-docker-as-a-non-root-user). | ||
|
|
||
| ### Configure Docker to start on boot | ||
| ```bash | ||
| sudo systemctl enable docker | ||
|
|
||
| # To disable this behavior, use disable instead. | ||
| sudo systemctl disable docker | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Clear all Docker unused objects (images, containers, networks, local volumes) | ||
| ```bash | ||
| docker system prune # Clear all | ||
| docker system prune -a # Clear all (includes unused and dangling containers) | ||
|
|
||
| # By default, volumes are not removed to prevent important data from being deleted if there is currently no container using the volume. Use the `--volumes` flag when running the command to prune volumes: `docker system prune -a --volumes` | ||
|
|
||
| docker image prune # Clear unused images | ||
| docker container prune # Clear unused containers | ||
| docker volume prune # Clear unused volumes | ||
| docker network prune # Clear unused networks | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Docker Compose. Basic commands | ||
| More info about Docker Compose commands at [docker compose reference](https://docs.docker.com/compose/reference/). | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| # Basic. All containers or specific container: <container> | ||
| ## Starts existing containers for a service. | ||
| docker compose start <container> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Restarts existing containers/container for a service. | ||
| docker compose restart <container> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Stops running containers without removing them. | ||
| docker compose stop <container> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Pauses running containers of a service. | ||
| docker compose pause <container> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Unpauses paused containers of a service. | ||
| docker compose unpause <container> | ||
|
|
||
| # Display the logs of a container. Is it possible to retrieve only the last n seconds or other | ||
| docker logs [--since 60s] <container> -f | ||
|
|
||
| ## Lists containers. | ||
| docker compose ps | ||
|
|
||
| ## Remove all docker compose project | ||
| docker compose rm <container> | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # Build. | ||
| ## Builds, (re)creates, starts, and attaches to containers for a service. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up | ||
|
|
||
| ## Build & up all the containers. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up -d --build | ||
|
|
||
| ## Build & up an specific container. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] up -d --build <container> | ||
|
|
||
| ## To avoid using a cache of the previous build while creating a new image. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] build --no-cache | ||
|
|
||
| ## Build a project with a specific Docker Compose prefix. | ||
| docker compose [-f <docker compose-file>] -p <my_project> up -d --build | ||
|
|
||
| ## Log the build | ||
| docker compose build --no-cache &> docker_build.log | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # Down | ||
| # Stops containers and removes containers, networks, volumes, and images created by up. | ||
| docker compose [-p <my_project>] down | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Oops, something went wrong.